Today is our topic of discussion Vitamin C
Vitamin C

Definition
Vitamin-C is an essential nutrient for certain animals including humans. The term vitamin C encompasses several vitamers that have vitamin-C activity in animals. Ascorbate salts such as sodium ascorbate and calcium ascorbate are used in some dietary supplements. These release ascorbate upon digestion.
Ascorbate and ascorbic acid are both naturally present in the body, since the forms interconvert according to pH. Oxidized forms of the molecule such as dehydroascorbic acid are converted back to ascorbic acid by reducing agents.
Vitamin C functions as a cofactor in many enzymatic reactions in animals (including humans) that mediate a variety of essential biological functions, including wound healing and collagen synthesis. In humans, vitamin-C deficiency leads to impaired collagen synthesis, contributing to the more severe symptoms of scurvy.
Another biochemical role of vitamin C is to act as an antioxidant (a reducing agent) by donating electrons to various enzymatic and non-enzymatic reactions. Doing so converts vitamin-C to an oxidized state – either as Sem dehydroascorbic acid or dehydroascorbic acid. These compounds can be restored to a reduced state by glutathione and NADPH-dependent enzymatic mechanisms.
In plants, vitamin-C is a substrate for ascorbate peroxidase. This enzyme utilizes ascorbate to neutralize excess hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by converting it to water (H2O) and oxygen.

Sources:
Plant source :
Citrus fruits-orange, lemon, guava, pineapple, papay, blackberry, strawberry. tomato, cabbage, cauliflower, green peppers, lettuce etc.
Animal source –
Very poor. Milk contains small amount.
Functions:
1. It helps in formation of intercellular substance and tissue collagen.
2. It takes part in wound healing.
3. It is essential for maturation of RBC.
4. It prevents scurvy.
Effects of deficiency:
Scurvy and anaemia
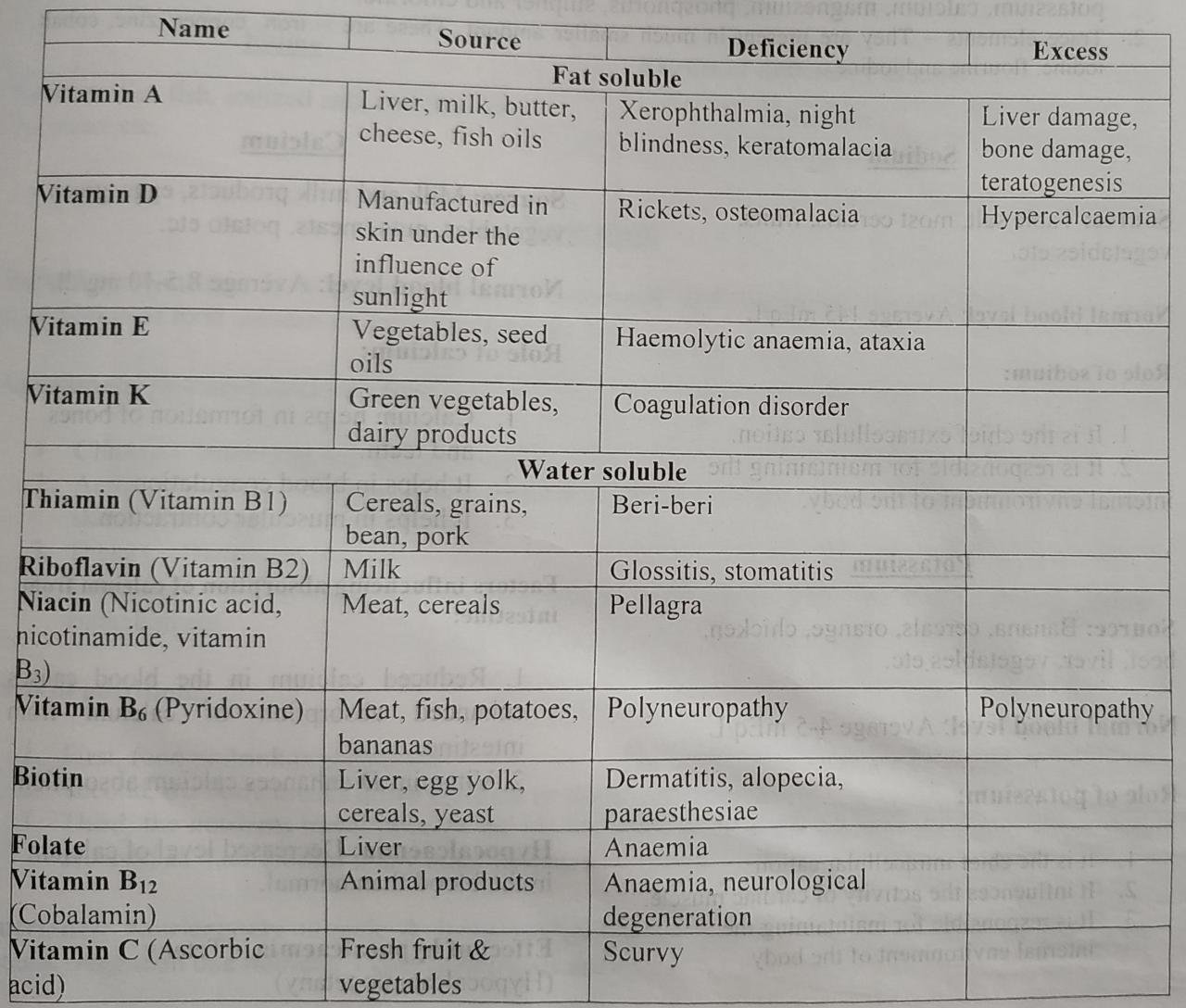
Summary of vitamins in table
See also :

1 thought on “Vitamin C ”