Today is our topic of discussion Protein Energy Malnutrition
Protein Energy Malnutrition
Definition:
Protein-energy malnutrition refers to a form of malnutrition where there is inadequate protein intake. The types of PEM are :
1. Kwashiorkor (protein malnutrition predominant) – weight for age < 60% expected
2. Marasmus (deficiency in both calorie and protein nutrition) – weight for age < 80% + edema
3. Marasmic Kwashiorkor (marked protein deficiency and marked calorie insufficiency signs present, sometimes referred to as the most severe form of malnutrition) – wt for age <60% + edema
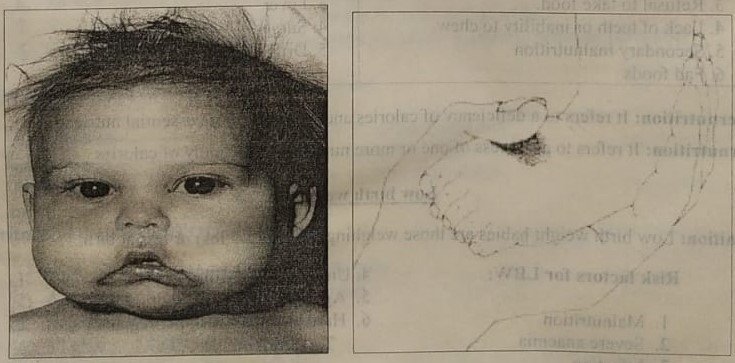
A )
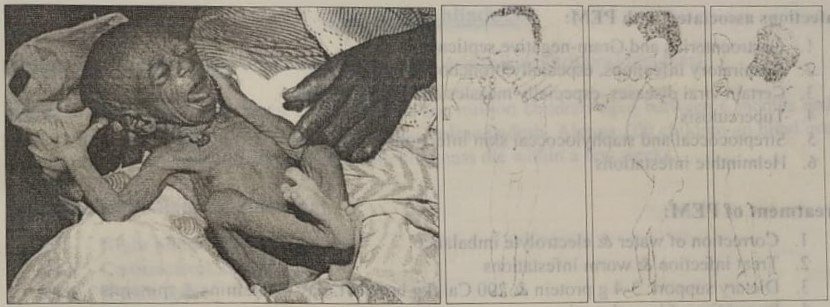
B )
Fig. 5-1: Photo of child with A) kwashiorkor and B) marusmus
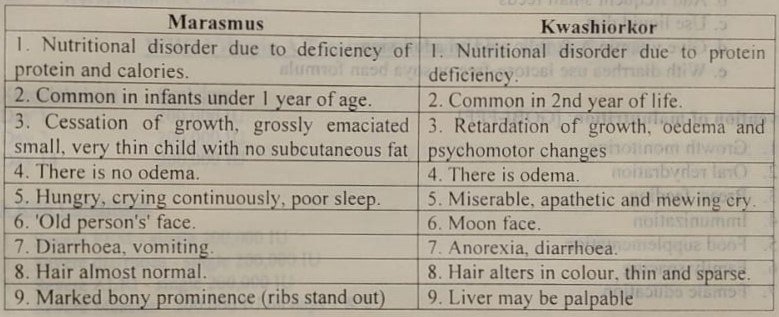
Difference between marasmus and Kwashiorkor
Precipitating factors for PEM:
1. Lack of food (famine, poverty)
2. Inadequate breast feeding
3. Wrong concepts about nutrition
4. Diarrhoea & malabsorption
5. Infections (worms, measles. TB)
Complication of PEM:
1. ARI
2. Diarrhoea
3. Hypoglycemia
4. Hypothermia
5. Hypokalemia
6. Hyponatremia
7. Heart failure
8. Infections (bacterial, viral & thrush)
Infections associated with PEM:
1. Gastroenteritis and Gram-negative septicaemia
2. Respiratory infections, especially bronchopneumonia
3. Certain viral diseases, especially measles and herpes simplex
4. Tuberculosis
5. Streptococcal and staphylococcal skin infections
6. Helminthic infestations
Treatment of PEM:
1. Correction of water & electrolyte imbalance
2. Treat infection & worm infestations
3. Dietary support: 3-4 g protein & 200 Cal /kg body wt./day + vitamins & minerals
4. Prevention of hypothermia
5. Counsel parents & plan future care including immunization & diet supplements
6. Feeding practice should be –
a. Continue breast feeding
b. Add frequent small feeds
c. Use liquid diet
d. Give vitamin A & folic acid on admission tab of sub obrozib lenitivu
Prevention of malnutrition:
[GOBI-FFF]
1. Growth monitoring
2. Oral rehydration
3. Breast feeding
4. Immunization
5. Food supplementation
6. Family spacing

7. Female education
See also :
