Today is our topic of discussion Methods of excreta/nightsoil disposal
Methods of excreta/nightsoil disposal
A. In unsewered areas:
1. Service type (conservancy system): Excreta is collected from commode manual labour for disposal.
[Question: Classify latrine?
Answer: The following points 2 & 3]
2. Non-service type (or sanitary latrines):
a. Pit latrine
b. Water-seal latrine
c. Bore hole latrine d. Septic tank latrine
e. Aqua privy: It is a single pit latrine which has a watertight pit filled with water. Excreta drop into the pit and wastewater is displaced into a storage chamber or a sewer line.
f. Water closet/flush toilet: It is usually made of ceramic material. The flush toilet consists of a tank that supplies flush-water for carrying away the excreta and a bowl into which the excreta are deposited. It also needs connection to constant running water and a discharge pipe to take the wastewater away to a sewer or septic tank. It is used in government offices, some schools and health facilities. molava sgnitio-100w dgo
3. Latrines suitable for camps, fairs (mela), mass gathering and temporary use:
a. Pit latrine: Suitable for temporary use by small group of people in rural areas.
b. Bore hole latrine: Suitable for temporary use by small group of people in rural areas.
c. Shallow & deep trench latrine: Suitable for temporary use by a large group of people in bottiman camps and fairs.
d. Chemical closet: It consists of a metal tank containing disinfectant fluid. In addition, a water dye and a deodorant are usually incorporated. The sits rest on the top of the tank. It is suitable for aircrafts and motor coaches.

Fig: Chemical closet toilet
B. In sewered areas:
Having methods of water disposal through water-carriage system (piped sewer lines) and treatment (primary and secondary) of sewage –
1. Primary treatment:
a. Screening
b. Removal of grit
c. Plain sedimentation
2. Secondary treatment:
a. Trickling filters
b. Activated sludge process
3. Dumping through water carriage system:
a. Sea outfall
b. River outfall
c. Sewage farming (land treatment)
d. Oxidation ponds & ditches
[Question: What are the methods of water disposal?
Answer: Water disposal are achieved by –
1. Treatment of sewage: Primary treatment & secondary treatment
2. Dumping through water-carriage system
Both the points described above under the heading ‘In sewered areas’]
Advantages and disadvantages of pit latrine
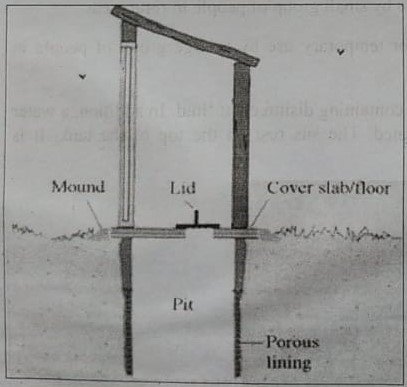
Fig: 2-1: Simple ‘pit’ latrine
Advantages:
1. It isolates excreta from environment prevent transmission of faeco-orally transmitted diseases.
2. They do not require water so are appropriate in areas where there is no adequate water supply.
3. Squatting is easy and acceptable to many users.
4. Alternating double pits allow the excreta to drain, degrade and transform into a safe humic material that can be used to improve soils.
5. They avoid contamination of surface water and top soil if properly installed and maintained.
6. They can be constructed with minimum cost using local material and local skills.
7. Presences of properly constructed slabs allow easy cleaning and avoid flies and unsightliness.
Disadvantages:
1. There may be a foul odour from the pit and they can be a favourable place for the breeding of flies and mosquitoes.
2. With single pits, a new pit needs to be dug
every time one gets full.
3. They can be susceptible failure/overflowing during floods.

See also :

1 thought on “Methods of excreta/nightsoil disposal”