Today is our topic of discussion human Environment
Human Environment

Definition:
All that which is external to the individual human host. living and non-living, and with which he is in constant interaction. This includes all of man’s external surroundings such as, air. water, food, housing, etc. It has three components:
Physical environment –
It means non-living things and physical factors, such as air, water, soil, housing, climate, geography, heat, light, noise, debris, radiation etc.
Biological environment –
It means the universe of living things (e.g., virus, bacteria, animals. plants, insects etc.) which surrounds man, including man himself.

Psychosocial environment –
It means ‘those factors affecting personal health, health care and community well-being that stem from the psychosocial make-up of individuals and the structure and functions of social groups’. These include cultural values, customs. beliefs. habits. attitudes. moral, religion, education, life-style, health services etc
Natural history of disease
Definition:
It refers to the progress of a disease process in an individual over time without any intervention. sensail to angia sidusi zull The process begins with exposure to or accumulation of factors capable of causing disease. Without medical intervention, the process ends with recovery, disability or death.
Importance:
Knowledge of the natural history of disease is fundamental for effective prevention.
Phases:
It comprises two phases –
Prepathogenesis phase:
It is a preliminary period of disease in man. The disease agent has not yet entered man, but the factors which favor its interaction with the human host already exist in the environment. The causative factors of disease are regarded as agent, host & environment, or the ‘epidemiological triad’. The mere presence of these three factors in the prepathogenesis period is not sufficient to start the disease. There must be interaction of these three factors to initiate the disease process.
Pathogenesis phase:
It begins with the entry of the disease agent into the susceptible human host. The further events in this phase are clear cut in infectious diseases. The pathogenesis phase may be modified by intervention measures such as immunization & chemotherapy.
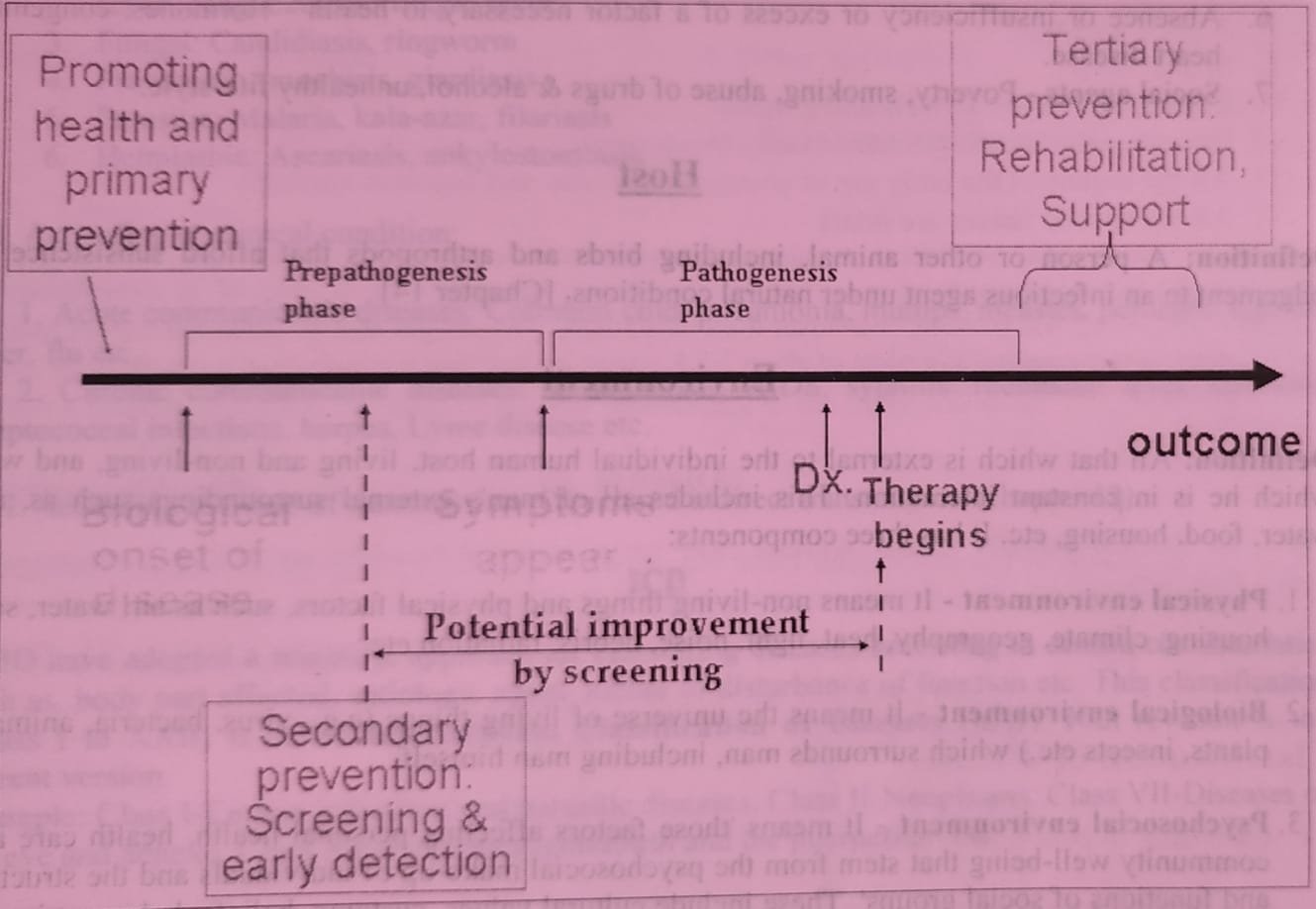
Fig: Natural history of disease and its relation with prevention
Stages of disease development:
- Incubation period: Pathogen is multiplying
- Prodromal period: Symptoms being to appear to resting sit of a nouinis
- Illness: Visible signs of disease.
- Period of decline: Pathogen is under control
- Period of convalescence: Patient begins to recover
See also :
