Today is our topic of discussion Health Cholesterol
Health Cholesterol

- These are not truly fat but distributed within body tissues as combination with fatty acids forming esters.
- It is widely distributed in all cells of the body, especially in the nervous tissue.
- It is the parent compound of all steroids synthesized in the body.
- Though it is necessary for our body but excess cholesterol are deposited in different tissues and may actually produce some diseases, such as gallstone, coronary artery blockage, peripheral vascular disease etc.
- They may also get attached with triglyceride and proteins in various proportions. These complex lipids are called lipoproteins. They are present normally within the body though all of them are not absolutely essential.
- One of the lipoproteins, called HDL (high density lipoprotein) is beneficial for our health, because it carrys peripheral cholesterol to the liver for excretion through bile. So, presence of more HDL-cholesterol or HDL in blood indicates wellbeing.
- Other lipoproteins are LDL (low density lipoprotein), VLDL (very low density lipoprotein) etc
- Presence of VLDL & LDL in excess indicates more cholesterol deposited in peripheral tissues & so, fat intake should be restricted.
Phospholipids:
Phospholipids are the complex lipids forming structural lipid of cell membrane.
Glycolipids:
Glycolipids are complex lipids which are also essential component of cell membrane.

Soap:
These are sodium or potassium salts of higher fatty acid (e.g, stearic acid).
Steroid:
The term ‘steroid’ includes many compounds which have a common chemical substance. the ‘steroid nucleus’. Cholesterol is the parent substance for all steroids synthesis. Example: Sex hormones, adrenocortical hormones etc.
RDA/Recommended Daily (or dietary) Allowance:
Recommended daily (or dietary) allowance is dout the quantity of a particular nutrient which should be consumed daily in order to maintain good health.
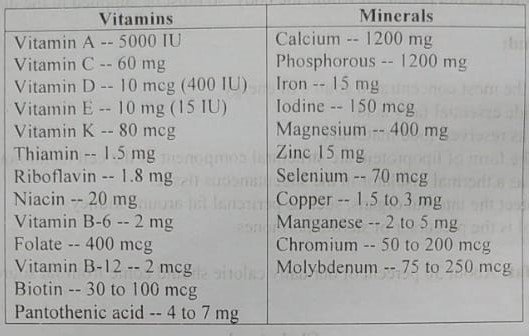
Average RDA of vitamins and minerals
See also :
