Today is our topic of discussion Definition of Pinworm
Definition of Pinworm

Definition:
Infection of intestine by Enterobius vermicularis (or pin-worm) is called enterobiasis.
Geographical distribution:
The pinworm has a worldwide distribution & not associated with gender, social class, race or culture. Pinworms are common in children. Finger sucking has been shown to increase incidence and relapse rates, and nail biting similarly associated.
Spreads from host to host through contamination, common among people living in close contact and tend to occur in all people within a household. Pinworms are an exception to belief, that intestinal parasites are uncommon in affluent society.
Epidemiological features:
Agent:
Enterobius vermicularis
Habitat:
Caecum and vermiform appendix, lay egg on perianal region.
Reservoir of infection:
Humans
Human habit:
perianal itching and nail biting, indiscriminate defaecation habit.
Period of communicability:
Until stool are negative.
Mode of transmission:
1. -Eating contaminated food and drink.
2. -Autoinfection
3. -Retrograde infection.
4. -transmission from man to man
Life cycle:
Eating food & drinks contaminated with eggs Passes to small intestine Egg shell is dissolved by digestive juice → Larva comes out and mature to adult worm → Male fertilizes the female and dies → Gravid female migrates to caecum and appendix → Eggs developed there→ The female passes down the rectum,
anus→ Comes outside and lays egg in perianal region → Eggs contaminate hands and food→→ Taken up by same host or other host→ Cycle is repeated. The whole cycle takes about 2-4 weeks.
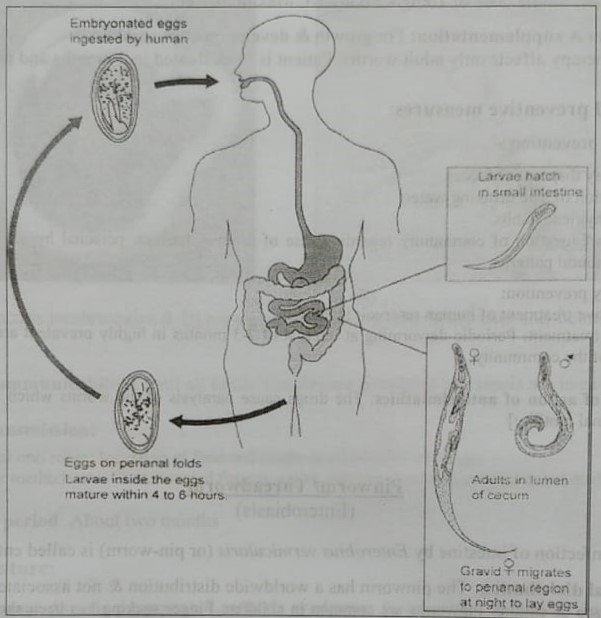
Fig: Life cycle of pinworm
Symptoms and signs:
1. Difficulty sleeping due to intense perianal itching at night.
2. Irritability (Due to itching and interrupted sleep)
3. Irritated or infected skin around the anus, from constant scratching
4. Irritation or discomfort of the vagina in young girls (adult worm enters vagina rather than anus)
5. Loss of appetite and weight (uncommon, but can occur in severe infections)
6. Pinworms can be spotted in the anal area, especially at night when the worms lay their eggs
7. Nocturnal enuresis
Treatment:
1. Tab. Albendazole (400 mg) for 26 years, single dose; kills the pinworms (not the eggs) & more than one household member is likely to be infected, so the entire household should be treated,
2. The treatment repeated after 2 weeks; this treats worms that hatched since the first treatment
Complications:
1. Acute appendicitis
2. Pelvic inflammatory disease
3. Vaginitis
Prevention and control:
1. To control the eggs, clean toilet seats in the high comode toilets daily.
2. Keep fingernails short and clean
3. Wash all bed linens twice a week
4. Wash hands before meals and after using the toilet
5. Avoid scratching the area around the anus. This can contaminate the fingers and the individual touch afterwards
everything else that
6. Keeping hands and fingers away from the nose and mouth unless they are freshly washed