Today is our topic of discussion Air Ventilation
Air Ventilation
Generally, it means the process or act of supplying a house or room continuously with fresh air.
Definition :
Ventilation is a science of maintaining atmospheric conditions which are comfortable and healthful to the human body.
Cross ventilation :
The circulation of fresh exterior air through an inlet (windows, doors, or other openings) with simultaneous forcing of interior air out of the building or room through an outlet (window, door, or other openings).
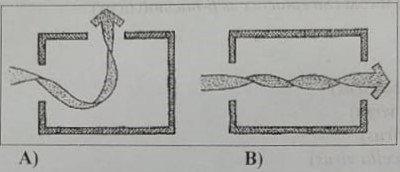
Fig: Cross ventilation A) two openings, adjacent wall & B) two openings, opposite wall
Purpose of ventilation:
1. To replace vitiated air.
2. To supply oxygen and fresh air.
3. To control temperature and humidity in order to provide thermal environment.
4. To dilute air-borne contaminations to an acceptable concentration.
Types of ventilation:
A. Natural ventilation:
Wind:
Winds are important and powerful among other types of natural ventilation.
Diffusion:
Air passes through the smaller openings or spaces by diffusion. This ensures mixing of gaseous impurities with fresh air and thus reduces the pollution in air. This is a slow process.
Temperature differences:
Air at high temperature expands and rises up and its place is taken by fresh cool air. This is more practical in cold climate than in hot climate.
B. Mechanical ventilation:
1. Exhaust ventilation: Air is extracted from a room by exhaust fans.
2. Plenum ventilation: Air is blown into a room by centrifugal fans.
3. Balanced ventilation: It is a combination of exhaust and plenum type of ventilation.
4. Air conditioning: It is the process of treating air so as to control simultaneously its temperature. humidity, cleanliness and distribution to meet the requirements of the conditioned space.
Standards of ventilation:
Cubic space:
A space of 1000-1200 cft. per person is sufficient.
Air change:
It is a more acceptable standard than the cubic space standard. In living rooms, there should be 2 to 3 air changes and in work rooms 4 to 6 air changes in one hour duration is recommended.
Floor space:
Optimum floor space requirement per person vary from 50 to 100 sq. ft. Recommended standard of floor space per adult person in a general hospital is 10 sq. meters.

Criteria of good ventilation:
1. It should prevent chilling and and drying of the body as well as stagnation of the body heat.
2. It should be able to remove the gases, odours, bacteria, dust etc. which contaminate the air. Good ventilation dilutes and removes these impurities which are produced due to vitiating process.
Effects of good ventilation:
1. It helps to maintain constancy of the body heat by maintaining homeostasis.
2. It helps to prevent air borne diseases such as, tuberculosis, chicken pox, diphtheria, measles, streptococcal infection (rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease) etc.
3. It helps to maintain calm and comfortable working environment.
Effects of ill-ventilation:
Effects of ill-ventilation or over-crowding in a room are –
1. Rise in room temperature
2. Increase in humidity go
3. Unpleasant body odour
4. Increased bacterial pollution
Health hazards due to ill-ventilation:
1. Headache
2. Drowsiness
3. Lassitude
4. Inability to concentrate
5. Depression
6. Feeling of fatigue
7. Increased chance of communicable diseases
Soil
Source of soil pollution:
1. Household wastes
2. Rotten food
3. Carcasses of animals and birds
4. Industrial wastes
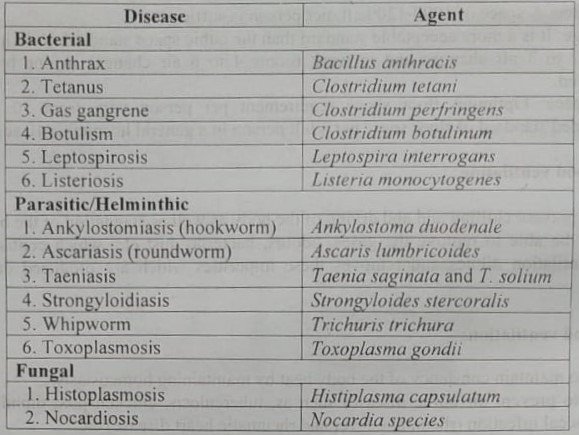
Table 4: Soil-borne diseases with their agents
See also :
