Today is our topic of discussion Definition of Rabies
Definition of Rabies

Rabies:
Rabies is an acute, highly fatal zoonotic disease involving central nervous system, caused by rabies virus.
Hydrophobia:
A set of symptoms at the later stage of rabies, in which the victim has difficulty swallowing, shows panic when presented with liquids to drink, and cannot quench its thirst.
Rabies and Bangladesh:
- 100% fatal but 100% preventable by modern management.
- Dog is the main source of rabies in 99% cases.
- inses bmaqolavab yiwole amoo A daterad to sta
- >2000 people die of rabies each year.
- Affected populations are mostly school going children (<15 years age).
- Over 85% rabies cases are rural poor people. – owl sidey to any lesini
- Few people still use the traditional method by kabiraj, boidya, oozhan etc.
- Most cases occur during the August and September, the mating season of dogs.
Agent:
Rabies virus (RNA virus, genus Lyssavirus in the family Rhabdoviridae).
Host:
All mammals including man.
Environment:
Any time but more prevalent in summer (mating season)
Reservoir:
a) Dog (99% of human infections)
b) Cat
c) Fox
d) Jackal
e) Mongoose
f) Wolf and other biting mammals
g) Other animals such as, cattle, pig, deer, horse, monkey etc. may also be reservoir.
Source of infection:
Saliva of rabid animals (all exposures in wild considered category III exposure).

Mode of transmission:
Animal bites:
Accidental bite or scratch by an infected animal.
Licks:
Saliva comes into direct contact with mucosa or fresh skin wounds.
Human-to-human:
Transmission by bite (evidence is present).
Others:
Rarely, by inhalation of virus-containing aerosol or transplantation of an infected organ.
Incubation period:
1-3 months (vary from <1 week to >1 year).
Pathogenesis:
Virus multiplies locally before attachment to nerve endings and through peripheral nerves to brain. Following infection of CNS, the virus causes an acute, progressive encephalomyelitis. Then it spreads through peripheral nerves to tissues – salivary glands, skeletal muscle, adrenal glands and skin.
Symptoms & signs:
Rabies is almost invariably fatal once clinical symptoms have developed –
Prodromal symptoms (3-4 days):
- Mild fever, headache, malaise and sore throat.
- Often pain or an unexplained tingling, pricking or burning sensation at the wound site.
Systemic manifestation:
Furious rabies (most patients):
a) Exhibit signs of hyperactivity & excited behaviour.
b) Hydrophobia (fear of water): On sight of water, spasm occurs on the muscles of swallowing. Hydrophobia is pathognomonic of rabies.
c) Photophobia (fear of light)
d) Aerophobia (fear of air): Elicited by a current of air across the face; cause violent spasms of the pharyngeal and neck muscles.
e) After a few days, death occurs by cardio-respiratory arrest.
Paralytic rabies (few cases):
Runs a longer course. The muscles gradually paralyzed, starting at the site of bite/scratch. A coma slowly develops, and eventually death. The paralytic form of rabies is often misdiagnosed, contributing to the underreporting of the disease.
[Clinical types of rabies: Two types – Furious rabies & Paralytic (dumb) rabies]
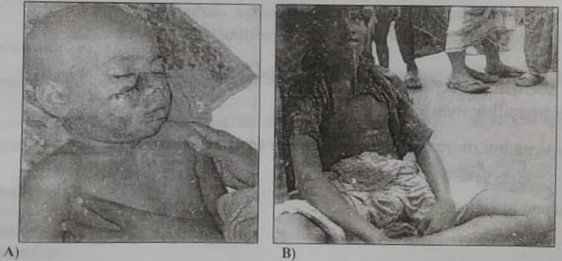
Fig: A) Category III dog bite & B) patient of rabies
See also :
